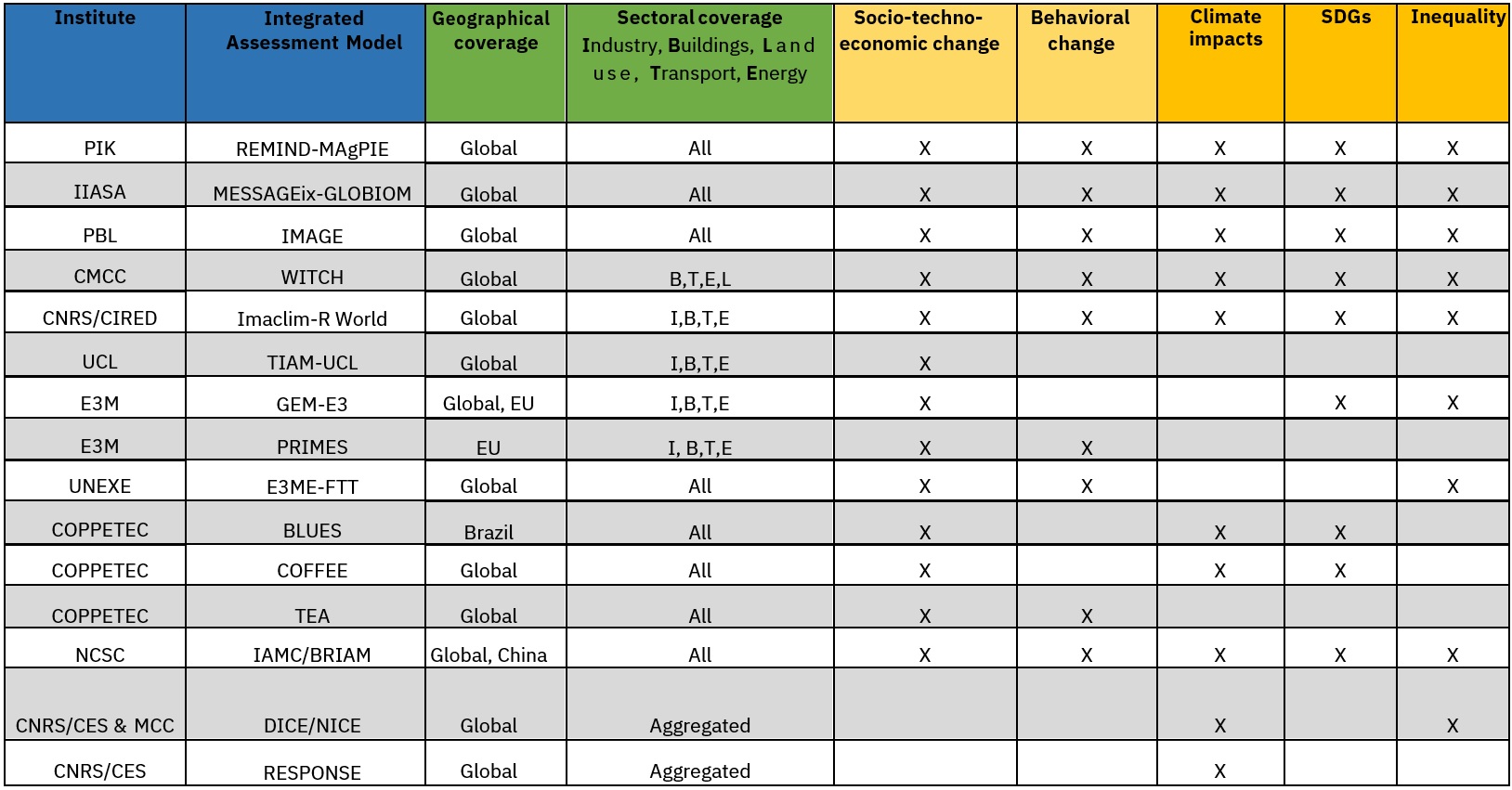
REMIND-MAgPIE (PIK)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
all (industry, buildings, transport, energy, land-use)
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
yes
Climate impacts:
yes
SDGs:
yes
Inequality:
yes
Further information:
Luderer et al (2015) Description of the REMIND Model (Version 1.6); Kriegler et al. (2017) Global Environmental Change 42: 297-315.
MESSAGEix-GLOBIOM (IIASA)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
all (industry, buildings, transport, energy, land-use)
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
yes
Climate impacts:
yes
SDGs:
yes
Inequality:
yes
Further information:
Grubler et al (2018) A low energy demand scenario for meeting the 1.5 °C target and sustainable development goals without negative emission Nat Energy 3:515–527
IMAGE (PBL)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
all (industry, buildings, transport, energy, land-use)
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
yes
Climate impacts:
yes
SDGs:
yes
Inequality:
yes
Further information:
van Vuuren et al (2017) Energy, land-use and greenhouse gas emissions trajectories under a green growth paradigm. Global Environmental Change 42:237–250
WITCH (RFF-CMCC)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
buildings, transport, energy, land-use
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
yes
Climate impacts:
yes
SDGs:
yes
Inequality:
yes
Further information:
Emmerling et al (2016) The WITCH 2016 Model – Documentation and Implementation of the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways, 2139/ssrn.2800970
Imaclim-R World (CIRED)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
buildings, transport, energy, industry
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
yes
Climate impacts:
yes
SDGs:
yes
Inequality:
yes
Further information:
Waisman et al (2012) The Imaclim-R model: infrastructures, technical inertia and the costs of low carbon futures under imperfect foresight, 10.1007/s10584-011-0387-z
TIAM-UCL (UCL)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
buildings, transport, energy, industry
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
no
Climate impacts:
no
SDGs:
no
Inequality:
no
Further information:
McGlade et (2015) The geographical distribution of fossil fuels unused when limiting global warming to 2 °C. Nature 517:187–190. doi: 10.1038/nature14016
GEM-E3 (E3M)

Geographical coverage:
global, EU
Sectoral coverage:
buildings, transport, energy, industry
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
no
Climate impacts:
no
SDGs:
yes
Inequality:
yes
Further information:
Parousssos et al (2015) Assessment of carbon leakage through the industry channel: the EU Technological Forecasting and Social Change 90, 204-219
PRIMES (E3M)

Geographical coverage:
EU
Sectoral coverage:
buildings, transport, energy, industry
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
yes
Climate impacts:
no
SDGs:
no
Inequality:
no
Further information:
Capros et al (2012) Model-based analysis of decarbonising the EU economy in the time horizon to Energy Strategy Reviews, Volume 1, Issue 2, pages 76-84.
E3ME-FTT (UNEXE)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
all (land use, buildings, transport, energy, industry)
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
yes
Climate impacts:
no
SDGs:
no
Inequality:
yes
Further information:
Mercure et al (2018) Environmental impact assessment for climate change policy with the simulation-based integrated assessment model E3ME-FTT-GENIE. Energy Strategies Review 20: 195–208.
BLUES (COPPETEC)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
all (land use, buildings, transport, energy, industry)
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
no
Climate impacts:
yes
SDGs:
yes
Inequality:
no
Further information:
Rochedo et al (2018) The threat of political bargaining to climate change in Nature Climate Change 8, 695-698.
COFFEE (COPPETEC)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
all (land use, buildings, transport, energy, industry)
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
no
Climate impacts:
yes
SDGs:
yes
Inequality:
no
Further information:
Rochedo (2016) Development of a global integrated energy model to evaluate the Brazilian role in climate change mitigation Doctoral thesis, COPPETEC/UFRJ, Brazil
TEA (COPPETEC)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
all (land use, buildings, transport, energy, industry)
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
yes
Climate impacts:
no
SDGs:
no
Inequality:
no
Further information:
Cunha et al (2017) Integrating General Equilibrium and Energy Models: a Methodological Proposal. In: 10th Annual Meeting of the IAMC, Recife, Brazil
IAMC/BRIAM (NCSC)

Geographical coverage:
global, China
Sectoral coverage:
all (land use, buildings, transport, energy, industry)
Socio-techno-economic change:
yes
Behavioural change:
yes
Climate impacts:
yes
SDGs:
yes
Inequality:
yes
DICE/NICE (CES/MCC)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
aggregate
Socio-techno-economic change:
no
Behavioural change:
no
Climate impacts:
yes
SDGs:
no
Inequality:
yes
Further information:
Dennig et al (2015) Inequality, climate impacts on the future poor, and carbon prices. PNAS 112, no. 52: 15827-32.
RESPONSE (CES)

Geographical coverage:
global
Sectoral coverage:
aggregate
Socio-techno-economic change:
no
Behavioural change:
no
Climate impacts:
yes
SDGs:
no
Inequality:
no
Further information:
Dumas et al (2012) Comprehensive description of RESPONSE, CIRED Working Paper 41